The subject to be explored by the team:
It is important to know how to evaluate the maturity of a technology very early on if it is to become the pillar on which a future business is to be based. This allows to better anticipate the resources and time that will be needed to validate the technical feasibility of the project before launching on the market.
A tool for collaboration:
The TRL scale is used to evaluate the maturity of a technology when the objective is to industrialize it. Popularized by NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense, it is often used by large organizations to frame calls for technology projects and therefore opportunities for public and private funding.
To go further :
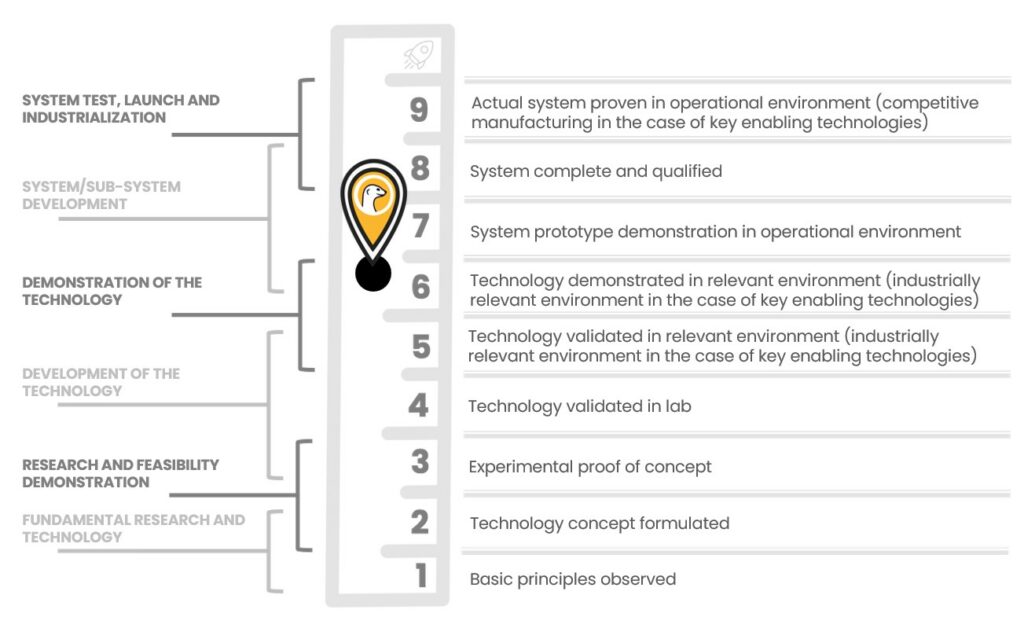
Here are definitions of each TRL stage according to the United States and the ANR (France):
TRL 1 level:
USA: Lowest level of technological maturity. Scientific research begins to translate into applied research and development. Examples may include paper studies of the basic properties of a technology.
France : C’est le niveau le plus bas de maturité d’une technologie. On commence à évaluer les applications militaires de la recherche scientifique, par exemple sous la forme de publications analysant les caractéristiques fondamentales de la technologie.
TRL 2 level:
USA: The invention begins. Once the basic principles are observed, practical applications can be invented. The application is speculative and there is no detailed evidence or analysis to support the hypothesis. Examples are always limited to paper studies.
France : Début de la phase d’invention. A partir de l’observation des principes de base, il devient possible d’envisager des applications pratiques. Ces applications restent potentielles. Il n’y a pas de preuve ni d’analyse détaillée pour les confirmer. On n’en est encore qu’au stade d’études papier.
TRL 3 level:
USA: Active research and development is initiated. This includes analytical and laboratory studies to physically validate the analytical predictions of the separate components of the technology. Examples include components that are not yet integrated or representative.
France : Lancement d’études analytiques et de travaux de laboratoire concernant la validation de certaines briques élémentaires de la technologie afin de valider concrètement les études prévisionnelles.
TRL 4 level:
USA: The basic technological components are integrated to establish that all parts work together. This is “low fidelity” compared to the final system. Examples include ad hoc integration of hardware in the lab.
France : Les constituants de base de la technologie ont été intégrés, mais sous une forme relativement « peu représentative » d’un système éventuel, par exemple sous forme d’un « maquettage » en laboratoire.
TRL 5 level:
USA: The fidelity of the technology increases significantly. Basic technology components are integrated with reasonably realistic elements so that the technology can be tested in a simulated environment. Examples include high fidelity laboratory integration of components.
France : La représentativité des sous-systèmes s’accroît nettement. Les briques élémentaires sont intégrées dans un ensemble complet permettant l’essai de la technologie dans un environnement simulé réaliste, par exemple sous forme d’une intégration de laboratoire « très représentative ».
TRL 6 level:
USA: The representative prototype model or system (well beyond the artifact tested in TRL 5) is tested in a meaningful environment. It represents a major advance in the demonstrated maturity of a technology. Examples include testing a prototype in a “high fidelity” laboratory or in a simulated operational environment.
France : On essaie dans un environnement représentatif un modèle représentatif ou un prototype de système, bien plus complet que ce qui a été testé à l’étape 5, et ceci représente une étape clé de démonstration de maturité d’une technologie, comme par exemple l’essai d’un prototype dans un laboratoire restituant de façon très précise les conditions d’environnement, ou les conditions d’emploi opérationnel.
TRL 7 level:
USA: Prototype in a planned system (or about to be planned). Represents a major advance over TRL 6, requiring the demonstration of a prototype system in an operational environment, such as an aircraft, vehicle… Examples include testing the prototype on a test aircraft.
France : Démonstration d’un système prototype conforme au système opérationnel, ou très proche. Représente une forte progression par rapport à l’étape 6, avec la démonstration d’un prototype réel, dans un environnement opérationnel, tel par exemple un véhicule ou une plate-forme aérienne, par exemple un aéronef banc d’essais. On recueillera à ce stade des informations pour obtenir l’aptitude au soutien de cette technologie.
TRL 8 level:
USA: The technology has been proven to work in its final form and with the expected conditions. In most cases, this TRL represents the end of development of real systems. Examples include developmental testing and evaluation of the system to determine if it meets the design specifications.
France : On a prouvé le fonctionnement de la technologie, sous sa forme finale, et dans les conditions d’emploi attendues. Cette étape est dans la majorité des cas la fin de la démonstration, avec par exemple les essais et l’évaluation du système au sein du système d’arme prévu, afin de savoir s’il respecte les spécifications demandées, y compris pour le soutien en service.
TRL 9 level:
USA: Real application of the technology in its final form and under mission conditions, similar to those encountered during operational and evaluation tests. In all cases, this is the end of the final bug-fixing aspects of real system development. Examples include the use of the system under operational mission conditions.
France : Etape d’application de la technologie sous sa forme finale, et en conditions de mission représentatives, telles que celles qui peuvent être rencontrées lors d’essais et d’évaluations opérationnels, et d’essais de fiabilité, ce qui inclut par exemple l’emploi dans des conditions de missions opérationnelles.